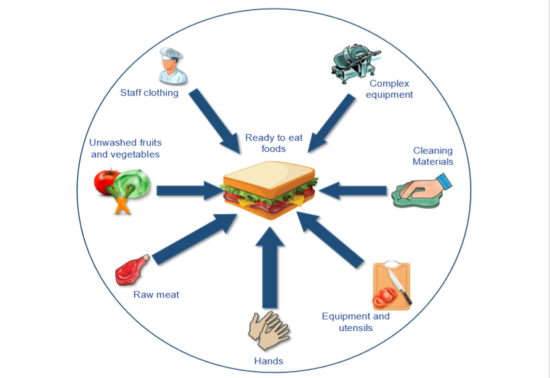
Cross-contamination occurs when harmful microorganisms are unintentionally transferred from one surface or substance to another, potentially contaminating previously safe or sterile items. This transfer can happen through direct contact, such as when raw meat comes into contact with ready-to-eat foods, or indirectly, such as when utensils or cutting boards used for raw meat are not properly cleaned before being used with other foods.
In food preparation, cross-contamination can lead to foodborne illnesses if pathogens from raw foods, such as bacteria like Salmonella or E. coli, are transferred to foods that are consumed raw or only lightly cooked. It’s essential to prevent cross-contamination by practicing proper food handling and sanitation techniques, including using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw meats and ready-to-eat foods, regularly washing hands and surfaces, and storing foods properly to prevent contact between raw and cooked items.
What is the cross-contamination procedure:
Cross-contamination in food handling can lead to foodborne illnesses, so preventing it is crucial. Here’s a procedure to minimize cross-contamination:
Handwashing: Always start by thoroughly washing your hands with soap and warm water before handling any food.
Separate Equipment: Have separate cutting boards, utensils, and equipment for raw meats, poultry, seafood, and ready-to-eat foods. Color-coded equipment can be helpful.
Separate Work Areas: Designate separate work areas for different types of foods, especially between raw and cooked items.
Storage: Store raw meats, poultry, and seafood on lower shelves or in separate containers to prevent juices from dripping onto other foods.
Clean and Sanitize: Regularly clean and sanitize all surfaces, utensils, and equipment, especially after handling raw foods.
Proper Thawing: Thaw frozen foods in the refrigerator, microwave, or under cold running water. Never thaw at room temperature to avoid bacterial growth.
Cooking Temperatures: Cook foods to their proper internal temperatures to kill harmful bacteria. Use a food thermometer to ensure accuracy.
Avoid Bare Hand Contact: Use gloves or utensils when handling ready-to-eat foods to prevent contamination from the hands.
Storage: Store cooked and ready-to-eat foods above raw meats, poultry, and seafood in the refrigerator to prevent cross-contamination from dripping juices.
Labeling: Clearly label and date all food items to ensure proper rotation and prevent confusion.
Training: Provide proper training to all staff members involved in food handling to ensure they understand the risks of cross-contamination and how to prevent it.
Monitor and Correct: Regularly monitor food handling practices and correct any issues immediately.
By following these procedures, you can significantly reduce the risk of cross-contamination and ensure the safety of the food you handle.
Food Safety and Foodborne Illness Prevention from the Home Kitchen: For Home Health Aides and Caregivers Kindle Edition

Disclaimer:
This post contains affiliate links which means I may receive a small commission if you purchase using that link at no extra cost to you. and if you do,
I appreciate you!